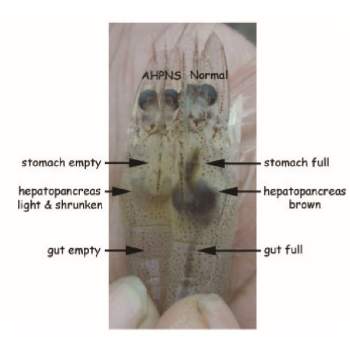
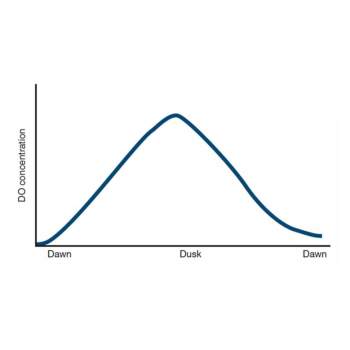
A shrimp crop calendar is a systematic timeline that guides farmers through the stages of shrimp farming, ensuring effective management, healthy shrimp growth, and optimal yields.
It includes activities categorized into pre-stocking, stocking, and post-stocking phases.
1. Pre-Stocking Phase :
Duration: 3–4 weeks
- Pond Preparation:
- Drying the pond to remove unwanted organisms and pathogens.
- Applying lime to adjust soil pH.
- Desilting and leveling the pond bottom.
- Water Preparation:
- Filling the pond with clean water and treating it with chlorine or other disinfectants.
- Adding probiotics to establish a favorable microbial environment.
- Fertilizing to promote the growth of natural feed (phytoplankton and zooplankton).
- Water Testing:
- Monitoring pH, dissolved oxygen, salinity, and temperature.
2. Stocking Phase
Duration: Initial stocking to Week 1
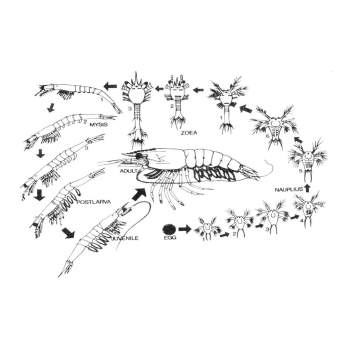
- Seed Selection:
- Procure disease-free and healthy post-larvae (PL) from a certified hatchery.
- Acclimatization:
- Gradually adapt the shrimp seeds to pond water temperature and salinity.
- Stocking:
- Stock the pond early in the morning or late evening to minimize stress on the shrimp.
3. Post-Stocking Phase
Duration: 3–5 months (depending on shrimp species)
Weekly Management Activities:
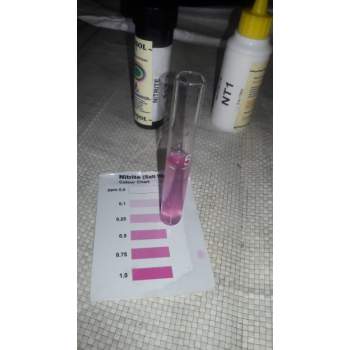
- Water Quality Monitoring:
- Check pH (6.8–8.5), dissolved oxygen (≥5 ppm), ammonia, and salinity levels regularly.
- Feed Management:
- Provide balanced feed (pellets) in multiple rations based on shrimp size and growth stage.
- Monitor feed conversion ratio (FCR).
- Pond Maintenance:
- Remove sludge periodically to prevent water contamination.
- Maintain aerators to ensure oxygenation.
4. Mid-Cycle Activities (Month 2–3):
- Shrimp Health Checks:
- Conduct routine sampling to monitor shrimp growth and detect diseases.
- Administer probiotics and other health supplements as needed.
- Water Exchange:
- Partial water exchange to maintain water quality.
5. Harvesting Phase
Duration: Final Month (Week 18–22)
- Pre-Harvest Preparation:
- Reduce feeding a few days before harvesting.
- Check market requirements (size and weight preferences).
- Harvesting:
- Use nets or drain the pond to collect shrimp.
- Transfer shrimp to ice immediately to maintain quality.
- Post-Harvest Pond Management:
- Clean and prepare the pond for the next cycle.
Advantages of a Shrimp Crop Calendar:
- Ensures timely completion of tasks.
- Reduces risk of diseases and crop loss.
- Optimizes feed and water management.
- Improves shrimp health and quality.
- Increases overall profitability.